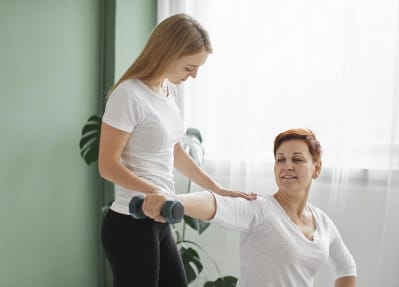An ankle fracture is a break in the tibia bone at the ankle joint and can limit your ability to perform routine activities such as walking and running. It is also referred to as a broken ankle, a painful injury that causes the loss of lower extremity strength, pain, and range of motion.
Awkward landings, contact sports injuries, and foot twisting falls are the leading causes of broken ankles. Simple to complex fractures can occur, ranging from a single medial or lateral malleolus fracture to an ankle dislocation with a bi- or trimalleolar fracture.
To fully regain functional mobility and resume your prior level of activity following a fractured ankle, physical therapy (PT) may be beneficial.
Symptoms and Causes
Such a fracture is a break or crack in one or more bones comprising the ankle joint. Fractures can appear in any of these bones, and the degree of the fracture can vary.
Symptoms
Pain: This kind of fracture cause severe discomfort, which can be acute and immediate at the time of injury. Movement or bearing weight on the afflicted ankle might exacerbate the pain.
Swelling: Due to damage to soft tissues and blood vessel disruption, the wounded ankle frequently swells quickly. Significant swelling might make the ankle appear larger than the side that is not affected.
Bruising: Bruising around the ankle can develop due to bleeding from damaged blood vessels.
Deformity: It can cause visible deformity or misalignment of the ankle joint. The ankle may appear crooked or out of place.
Instability: This fracture can lead to instability in the joint, making it difficult to bear weight or walk. You may feel like the ankle is giving way or is unable to support your body weight.
Tenderness: The injured ankle will be tender to touch, and pressing on specific areas may elicit pain.
Causes
Fall: Falling from a height or slipping on a surface can result in an these kind of fracture. It is a common cause, especially in older adults.
Twisting or rolling the ankle: Sudden twisting or rolling movements of the ankle can cause the bones to fracture. It can occur during sports activities or when stepping on an uneven surface.
Direct impact or trauma: A direct blow to the ankle, such as a fall, motor vehicle accident, or sports collision, can cause a fracture.
Repetitive stress: Overuse or repetitive stress on the ankle joint, particularly in athletes or individuals engaged in running, jumping, or repetitive motions, can lead to stress fractures over time.
Role Of Physical Therapy In Treatment
After the fracture has been somewhat reduced and immobilized, you can be recommended for this therapy, which is beneficial for learning how to use a cane, walker, or crutch as an assistive device.
To prevent the muscle groups that help you walk from becoming too weak while the fracture heals, you can practice gentle exercises for the knee and hip muscles. Once your fractured ankle has healed, your healthcare provider or expert will remove the cast. They allow you to bear more weight on your ankle and can suggest using assistive devices.
A therapist can assess your ankle at this stage so that the right course of treatment can be taken. The evaluation looked at gait, strength, pain, and range of motion. The therapist begins by applying cold, heat, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to the affected ankle areas to reduce pain and edema.
Exercises For Ankle Fracture
Image Resource Link: https://www.verywellhealth.com/physical-therapy-after-ankle-fracture-2696531
Physical therapy is essential to the overall treatment plan for an ankle bone fracture. It typically begins after the initial immobilization and healing phase, which may involve a cast, splint, or surgical intervention.
The goal of this therapy is to help restore strength, flexibility, balance, and function to the ankle joint. Here are some common interventions of this therapy for broken ankle:
1. Range of motion exercises
These exercises help restore the ankle joint’s normal range of motion. The physical therapist may guide you through gentle movements and stretches to improve flexibility and prevent stiffness.
2. Strengthening exercises
The muscles surrounding the ankle must be strengthened to maintain stability and ensure correct joint function. The therapist will provide exercises focusing on the calf muscles, ankle dorsiflexion (which lift the foot upward), and ankle plantar flexors (which push the foot downward) to increase strength and support.
3. Balance and proprioception training
An broken ankle can impact proprioception, body position awareness, and balance. The therapist will include activities to improve these abilities, such as standing on one leg, conducting balance drills on uneven surfaces, and using particular tools to challenge stability.
4. Gait training
Session of this therapy involves crucial components like walking and relearning good gait mechanics. The physical therapist will evaluate Your walking pattern and offer tips and exercises to help you return to your regular, effective gait.
5. Functional training
This therapy aims to help you regain the capacity to carry out particular functional tasks from your daily routine, job, or activity. To help you restore confidence and functionality, this may entail doing motions and functions that closely resemble your everyday activity.
6. Pain management techniques
During rehabilitation, therapists can use pain management techniques, including ice or heat therapy, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, or manual therapy, to reduce pain and inflammation.
7. Education and guidance
The therapist will guide you on the best body mechanics, how to move, and how to avoid being hurt again. They could also offer suggestions for suitable shoes and assistive technology if necessary.
A Word From Verywell
Your ability to walk, run, or fully engage in job and recreational activities may be significantly reduced due to an ankle fracture. Following such a fracture, physical therapy can help you regain mobility and return to your regular activities and functions securely.